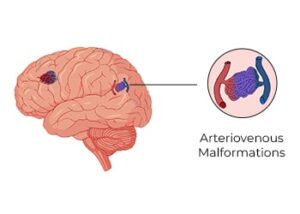
Cerebrovascular conditions
Aneurysms, vertebral stenosis, and intracranial stenosis are all types of cerebrovascular conditions, as are stroke and carotid stenosis.
Vessel constriction (stenosis), thrombosis, obstruction, or rupture of a blood vessel can all cause a reduction in blood flow (haemorrhage). In addition, a lack of blood supply to the brain (ischemia) can lead to a stroke.
Causes
There are no recognized causes of cerebrovascular anomalies. However, the following conditions can lead to cerebral stenosis or aneurysms:
- Diabetes
- Cholesterol levels are too high.
- Diabetic hypertension
- Obesity and lack of exercise
- Smoking
Symptoms
- A transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke typically isn’t the first sign of cerebrovascular stenosis. Trans ischemic attack or stroke symptoms may include the sudden onset of any or a combination of the following:
- Dizziness
- Nausea/vomiting
- Severe headache
- Insomnia, disorientation, difficulties understanding, and lapses in memory
- Arm or leg numbness or weakness
- Weakness or drooping of one side of the face
- Speech that is slurred or distorted
- Vision loss or inability to see
- Inability to walk due to a lack of coordination or balance
Diagnosis
The doctor will analyze your symptoms, risk factors, family and medical histories and do a physical exam to diagnose cerebrovascular illness. In most situations, the doctor will also prescribe imaging tests to evaluate the brain’s arteries and veins. This includes:
- Angiogram
- Ultrasound
- CT
- MRI
- EEG
Treatment
Treatment options for cerebrovascular illness may include lifestyle modifications, medication, careful monitoring, and surgery, depending on the kind and severity of the condition.
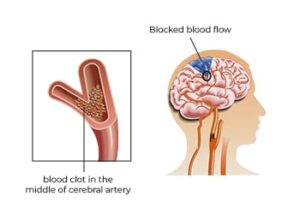
Ischemic Stroke
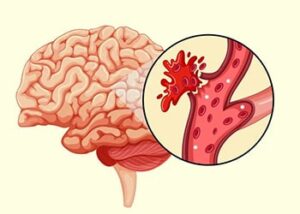
Hemorrhagic Stroke
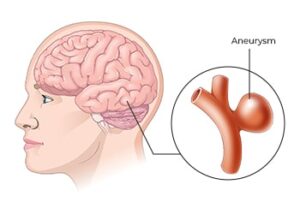
Cerebral Aneurysms
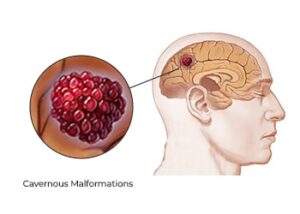
Cavernous Malformations
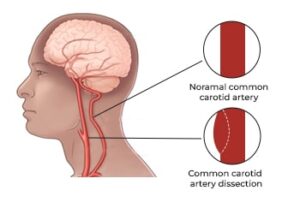
Carotid Dissection
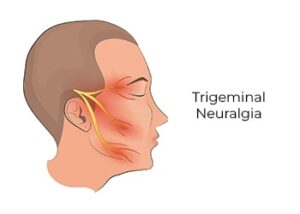
Trigeminal Neuralgia
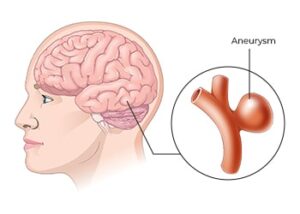
Cerebral Aneurysms